In this edition of the Windows Vista and Windows 7 Report, we show you how to change Windows 7’s Logon screen wallpaper.

While experimenting with several Microsoft Windows 7 systems recently, we spent a lot of time staring at the Logon screen. During that time, we began to think about changing the Logon screen wallpaper. Now, we have changed the Logon screen wallpaper in just about every version of Windows we’ve used, so we know that there had to be a way to do so.
When we began to investigate the procedure in Windows 7, we discovered that changing the Logon screen wallpaper in the newest version of the Windows operating system is easy, once you know the steps — and you don’t even need any third-party software to do it.
In order to make it easy for OEMs to customize Windows 7, Microsoft built the ability to change the Logon screen wallpaper right in to the operating system. In this edition of the Windows Vista and Windows 7 Report, we’ll show you how to change Windows 7’s Logon screen wallpaper.
A Registry tweak
The process begins with a very minor Registry tweak. Even for those who would not normally feel comfortable editing the Registry, this one’s a piece of cake. To begin, click the Start button and type Regedit in the Search box. Then, select the appropriate result and press [Enter]. When you do, you’ll see the User Account Control, shown in Figure A, and will need to click the Yes button.Note: Editing the Windows Registry file is not without its risks, so be sure you have a verified backup before making any changes.
Figure A
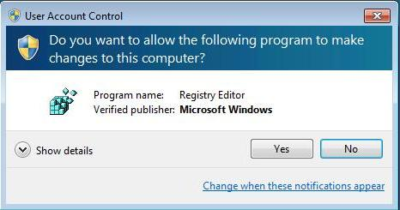
You will encounter a UAC when you launch the Registry Editor.
Once the Registry Editor launches, locate and right-click on HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key and select the Find command. When you see the Find dialog box, type OEMBackground in the text box and make sure that only the Values check box is selected, as shown in Figure B.
Figure B
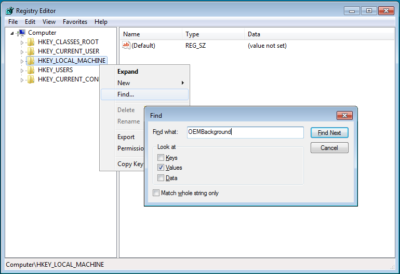
Type OEMBackground in the Find dialog box.
When the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI\Background key opens, locate and double-click the OEMBackground value. When you see the Edit DWORD dialog box, change the value data from 0 to 1, as shown in Figure C. (If the OEMBackground value doesn’t exist in the Background key, you’ll need to pull down the Edit menu from that key and select New | DWORD (32-bit) Value).
Figure C
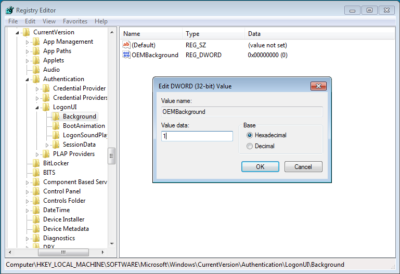
Change the value data from 0 to 1.
To complete this part of the operation, click OK to close the Edit DWORD dialog box and then close the Registry Editor.
Creating folders
In the second part of the operation, you’ll need to create a couple of folders. To begin, launch Windows Explorer. Then navigate to the C:\Windows\System32\Oobe folder. Once you access the Oobe folder, click the New Folder button in the Windows Explorer toolbar. You’ll see a confirmation dialog box, like the one shown in Figure D. When you click Continue, the new folder will be created and you can name it info.
Figure D
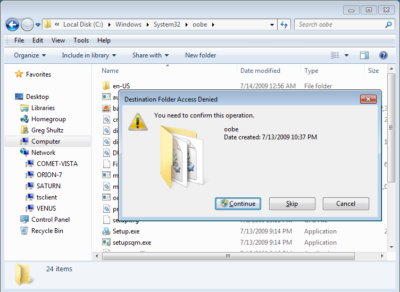
When you click the New Folder button, you’ll encounter a confirmation dialog box.
Then, open the info folder, click the New Folder button again, work through the confirmation dialog box, and then name the second new folder backgrounds.
Configuring the wallpaper
You can use any image that you want for your new Logon screen wallpaper. However, the image has to be in JPG format and you need to name it backgroundDefault.jpg. When you copy your file to the Windows\System32\Oobe\info\backgrounds folder, you’ll encounter and will need to work through a confirmation dialog box similar to the one shown in Figure D.
Two other things to keep in mind: First, the actual file size of backgroundDefault.jpg cannot exceed 256 KB. Second, you’ll want to use an image whose dimensions match the screen resolution that you are using. If you use a file whose dimensions are smaller, the image will be stretched and may appear distorted.
Altering shadows
As you know, the button and the text used to identify your user account on the Logon screen have shadows behind them to give them a 3D-like look, and these shadows work well with the default Logon screen wallpaper. Depending on what image you use for your new Logon screen wallpaper, these shadows might not work so well.
In addition to making it easy to change the Logon screen wallpaper, Microsoft also made it easy to adjust or disable the text and button shadows to accommodate your particular image.
To alter the shadows, launch the Registry Editor again as described above and access the
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI folder
Once you open the LogonUI folder, you’ll create a new DWORD value called ButtonSet, as shown in Figure E. You can then configure the shadow by setting the value data to one of the following numbers:
- 0 — Light shadow
- 1 — Dark shadow
- 2 — No shadow
Figure E
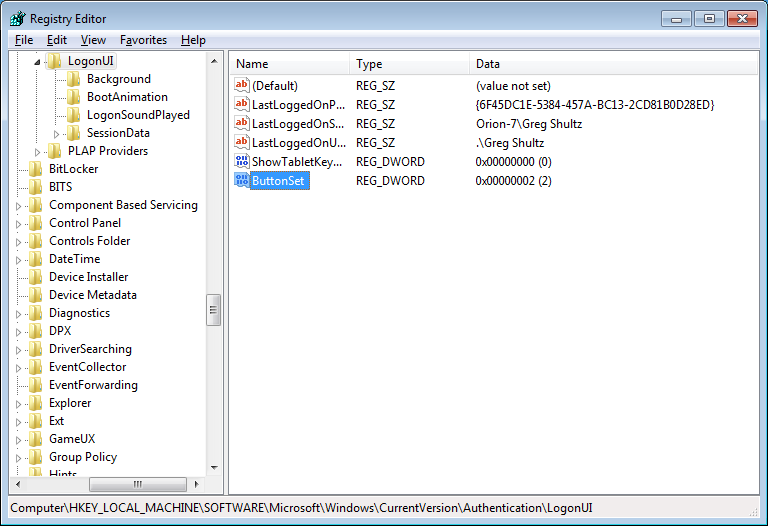
The ButtonSet value allows you to adjust or disable the text and button shadows.
Have questions?
Get answers from Microsofts Cloud Solutions Partner!
Call us at: 856-745-9990 or visit: https://southjerseytechies.net/
South Jersey Techies, LL C is a full Managed Web and Technology Services Company providing IT Services, Website Design Services, Server Support, Network Consulting, Internet Phones, Cloud Solutions Provider and much more. Contact for More Information.
To read this article in its entirety click here.